Accessing Organonitrogen Compounds via C-N Coupling in Electrocatalytic CO₂ Reduction
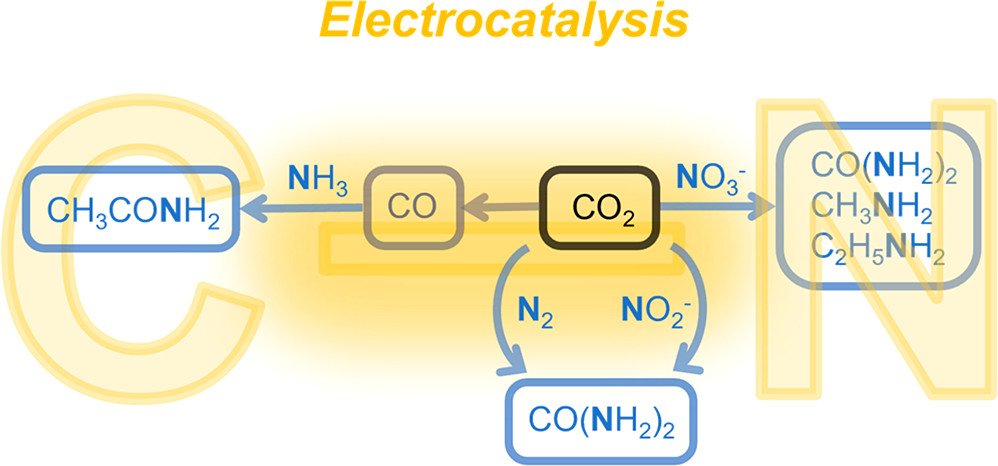
Given the limited product variety of electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction reactions solely from CO₂ and H₂O as the reactants, it is desirable to expand the product scope by introducing additional reactants that provide elemental diversity. The integration of inorganic heteroatom-containing reactants into electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction could in principle enable the sustainable synthesis of valuable products, such as organonitrogen compounds, which have widespread applications but typically rely on NH3 derived from the energy-intensive and fossil-fuel-dependent Haber-Bosch process for their industrial scale production. In this Perspective, research progress towards building C-N bonds in N-integrated electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction is highlighted, and the electrosyntheses of urea, acetamides, and amines are examined from the standpoint of reactivity, catalyst structure, and most fundamentally, mechanism. Mechanistic discussions of C-N coupling in these advances are emphasized and critically evaluated, with the aim of directing future investigations on improving the product yield and broadening the product scope of N-integrated electrocatalytic CO₂ reduction.
Tao, Z.; Rooney, C. L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, H. Accessing Organonitrogen Compounds via C-N Coupling in Electrocatalytic CO₂ Reduction. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2021, 143 (47) 19630-19642. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.1c10714