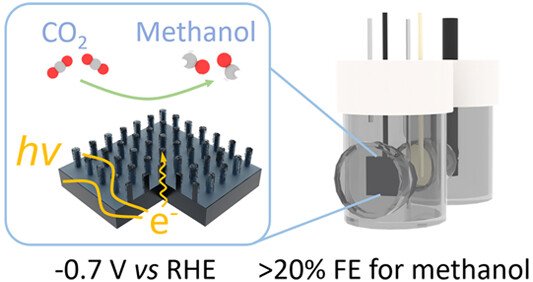
Tailoring Interfaces for Enhanced Methanol Production from Photoelectrochemical CO₂ Reduction
Efficient and stable photoelectrochemical reduction of CO₂ into highly reduced liquid fuels remains a formidable challenge, which requires an innovative semiconductor/catalyst interface to tackle. In this study, we introduce a strategy involving the fabrication of a silicon micropillar array structure coated with a superhydrophobic fluorinated carbon layer for the photoelectrochemical conversion of CO₂ into methanol. The pillars increase the electrode surface area, improve catalyst loading and adhesion without compromising light absorption, and help confine gaseous intermediates near the catalyst surface. The superhydrophobic coating passivates parasitic side reactions and further enhances local accumulation of reaction intermediates. Upon one-electron reduction of the molecular catalyst, the semiconductor–catalyst interface changes from adaptive to buried junctions, providing a sufficient thermodynamic driving force for CO₂ reduction. These structures together create a unique microenvironment for effective reduction of CO₂ to methanol, leading to a remarkable Faradaic efficiency reaching 20% together with a partial current density of 3.4 mA cm⁻², surpassing the previous record based on planar silicon photoelectrodes by a notable factor of 17. This work demonstrates a new pathway for enhancing photoelectrocatalytic CO₂ reduction through meticulous interface and microenvironment tailoring and sets a benchmark for both Faradaic efficiency and current density in solar liquid fuel production.
Shang, B.; Zhao, F.; Suo, S.; Gao, Y.; Sheehan, C.; Jeon, S.; Li, J.; Rooney, C. L.; Leitner, O.; Xiao, L.; Fan, H.; Elimelech, M.; Wang, L.; Meyer, G. J.; Stach, E. A.; Mallouk, T. E.; Lian, T.; Wang, H. Tailoring Interfaces for Enhanced Methanol Production from Photoelectrochemical CO₂ Reduction, J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2024, 146 (3), 2267-2274 https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.3c13540