Following CO and H Insertion into Ru–C Bonds with X-ray Photoelectron and Absorption Spectroscopies
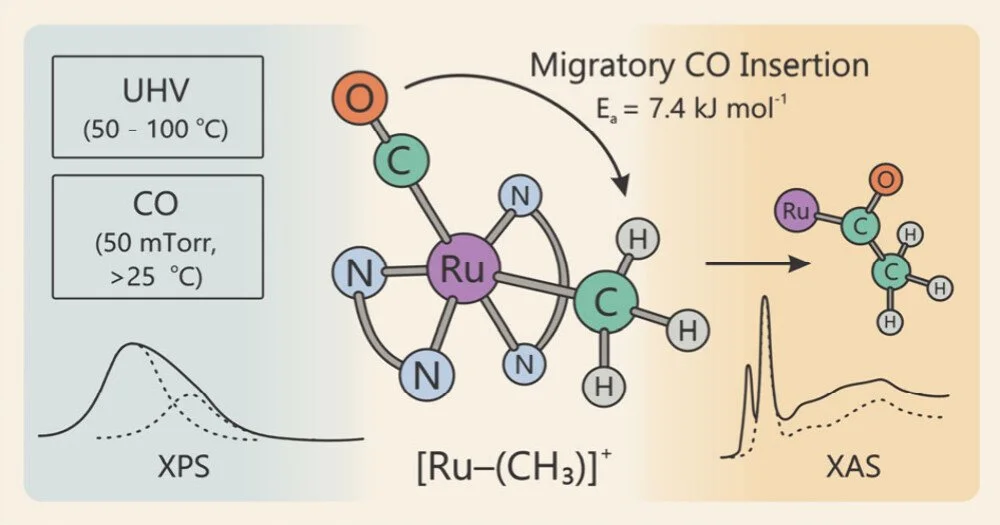
Insertion reactions play a central role in the catalytic synthesis of ethanol and higher alcohols. X-ray photoelectron and absorption spectroscopies have been used to follow migratory CO insertion and C─C coupling in a cis-[Ru(2,2′-bipyridine)₂(CO)(CH₃)]⁺ complex heated in a vacuum or exposed to CO. Heating of the Ru complex in a vacuum to temperatures above 50 °C induced spontaneous migration of CO into the Ru─CH₃ bond to yield a ─COCH₃ ligand. After adding CO to the background gas, the CO insertion reaction was seen at room temperature, opening the door for the synthesis of ethanol and more energy dense liquids.
Barba-Nieto, I.; Moncada, J.; Müller, A. V.; Rui, N.; Titus, C. J.; Jaye, C.; Meyer, G. J.; Concepcion, J. J.; Rodriguez, J. A. Following CO and H insertion into Ru-C bonds with X-ray photoelectron and absorption spectroscopies, Inorg. Chem., 2025, In press. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.5c03822