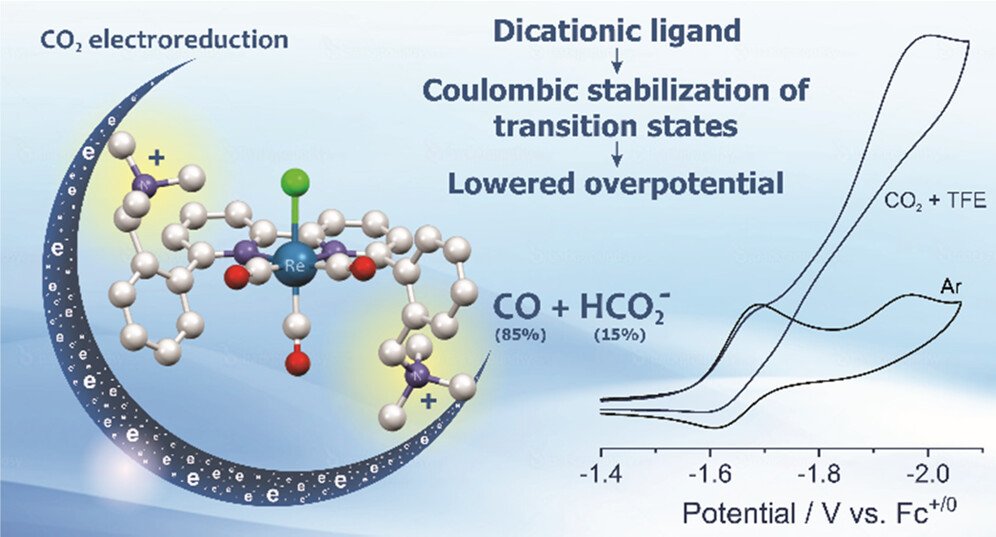
A Dicationic fac-Re(bpy)(CO)₃Cl for CO₂ Electroreduction at a Reduced Overpotential
A dicationic Re bipyridine-type complex, fac-Re(6,6′-(2-((trimethylammonio)-methyl)phenyl)-2,2′-bipyridine )(CO)₃Cl hexafluorophosphate (1²⁺), has been synthesized, and its electrochemical behavior under Ar and CO₂ has been investigated. The presence of pendent tetra-alkylammonium cations induces an anodic shift in the electrocatalytic potential for CO₂ reduction relative to structurally similar model complexes. The electrochemical mechanisms in anhydrous CH₃CN and in the presence of weak acids (water or trifluoroethanol) have been analyzed using cyclic voltammetry assisted by infrared spectroelectrochemistry and theoretical calculations. The dication enables catalysis at a diminished potential through Coulombic stabilization of the doubly reduced pentacoordinate species, its CO₂ adduct, the hydroxide anion, and the conjugate base formed during acid-assisted C–OH bond cleavage of the metallocarboxylic acid to the metallocarbonyl and H₂O. The major reduction product is CO, but in the presence of trifluoroethanol, formate is also produced with 14% Faradaic efficiency.
Rotundo, L.; Ahmad, S.; Cappuccino, C.; Polyansky, D. E.; Ertem, M. Z.; Manbeck, G. F. A Dicationic fac-Re(bpy)(CO)₃Cl for CO₂ Electroreduction at a Reduced Overpotential. Inorg. Chem. 2023, 62 (20), 7877-7889. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c00624