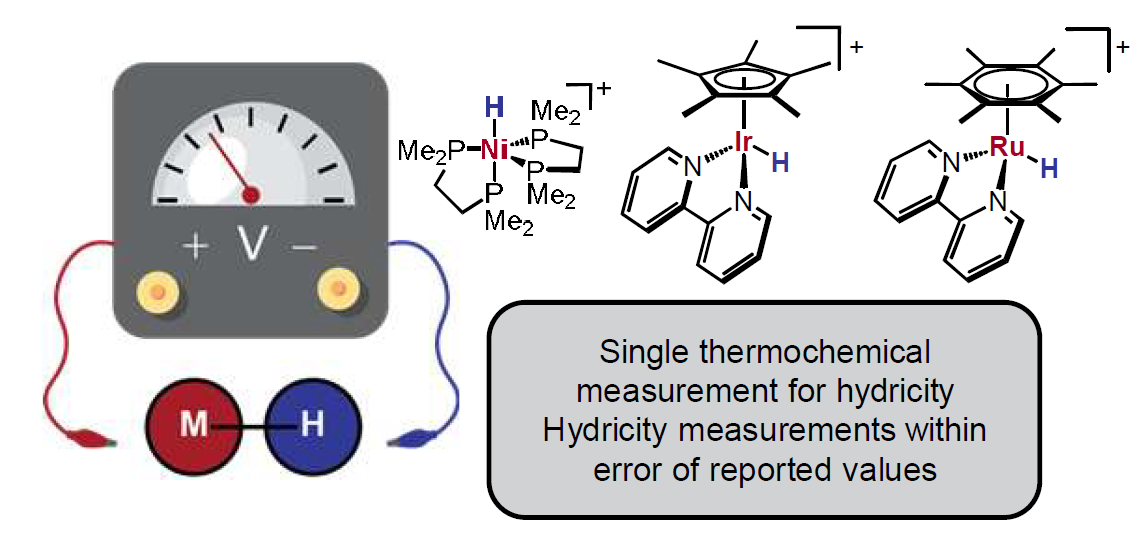
Open Circuit Potential Method for Thermodynamic Hydricity Measurements of Metal Hydrides
Metal hydrides are prevalent in many catalytic reactions, and thermodynamic hydricity has emerged as a useful parameter for understanding and predicting key hydride transfer steps with these intermediates. An open circuit potentiometry method for determining the hydricity of metal hydrides with a single thermodynamic parameter is reported. The open circuit potential (OCP) of a solution containing a metal hydride and its conjugate hydride acceptor, along with a conjugate acid/base pair, is coupled with known values for the acid pKₐ and H⁺/H⁻ reduction potential to determine the hydricity. The reliability of the method was established by using potentiometry to obtain the hydricity of three hydride complexes with varying supporting ligands and transition metal elements in acetonitrile solvent, all within error of previously reported values. Advantages and drawbacks of this method are discussed, and a recommended workflow for practitioners is introduced.
Smith, A. M.; Miller, A. J. M. Open Circuit Potential Method for Thermodynamic Hydricity Measurements of Metal Hydrides, Organometallics, 2024, 43 (24), 3163-3170. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.organomet.4c00144